ICMR - National Institute for Research
in Bacterial Infections
आईसीएमआर - राष्ट्रीय जीवाणु संक्रमण अनुसंधान संस्थान
Department of Health Research, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India
स्वास्थ्य अनुसंधान विभाग, स्वास्थ्य और परिवार कल्याण मंत्रालय, भारत सरकार
WHO Collaborating Centre For Research and Training On Diarrhoeal Diseases
NICED : Outbreak Investigations
प्रकोप जांच
प्रकोप जांच २०१६ -१७
बैक्टीरियोलॉजी और वायरोलॉजी डिवीजन के वैज्ञानिक द्वारा दिए गए सेवाएँ
राज्य के अनुरोध पर विभिन्न राज्य सरकारी अस्पतालों से स्वास्थ्य सम्पर्कित नमूनें प्राप्त हुआ तथा वायरल सीरोटाइपिंग के साथ डेंगू वायरस के निदान के लिए संसाधित किया गया था। लगभग सभी 12,000 बेजोड़ नमूने स्क्रीन किए गए हैं और राज्य स्वास्थ्य प्राधिकरण को सूचित करने के साथ संबंधित विभाग को प्रतिक्रिया परिणाम भेजे गए हैं।
पश्चिम बंगाल के विभिन्न दक्षिणी जिलों में फैले हुए दस्त के महामारी के दौरान, इस राज्य के विभिन्न हिस्सों से पीने योग्य जल स्रोतों के नमूनों के सूक्ष्म विश्लेषण और परीक्षा तथा सरकारी एजेंसियों को उसके परिणामों की रिपोर्टिंग, पर्यावरण प्रयोगशाला की एक नियमित गतिविधि रही है।.
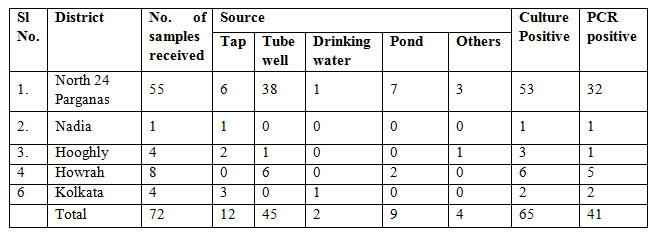
उत्तर 24 परगना, नदिया और हुगली, हावड़ा, कोलकाता और इसके आसपास के क्षेत्रों के विभिन्न PHC से पानी के नमूने प्राप्त हुए थे। इसके परिणाम संबंधित एजेंसियों को अवगत किया गया है तथा पश्चिम बंगाल सरकार के राज्य स्वास्थ्य सचिवालय को इस परिणाम का एक प्रतिलिपि भेजा गया है। रिपोर्ट के तहत अवधि के दौरान, विभिन्न सूत्रों से ७२ नमूने प्राप्त हुए थे, जिनमें से ५१ को मलीय कॉलिफॉर्म का उपस्थिति के लिए तथा २७ को V. Cholerae (तालिका 1) की उपस्थिति के लिए सकारात्मक पाया गया था|
तालिका 1: प्रकोप जल नमूने के जिलावार वितरण, उनके संबंधित स्रोतों और जीवों की पहचान की गई
प्रकोप जांच के लिए टीम के सदस्य: ए चक्रवर्ती
आदेश संख्या Z.28020/1/2017-EMR/AP (दिनांक २० फरवरी, २०१७) के
अनुसार, निदेशक द्वारा मनोनीत होने के पश्चात ; डॉ ए के
चक्रवर्ती ०१.०३.२०१७ तक मौसमी इन्फ्लुएंजा (H1N1) प्रकोप की
जांच के लिए २४ फरवरी, २०१७ को चित्तूर जिले गए| वह केंद्रीय
जांच दल के सदस्य थे और उन्होंने २४ फरवरी से १ मार्च, २०१७ तक
भारत में आंध्र प्रदेश के चित्तूर जिला में मौसमी इन्फ्लुएंजा
(H1N1) के प्रकोप की जांच की। इस यात्रा का लक्ष्य आंध्र
प्रदेश में H1N1 की बढ़ती प्रवृत्ति से संबंधित स्थिति की जांच
करना था। इंफ्लुएंजा / (H1N1) मामलों की घटनाओं की जांच
प्रारंभिक चेतावनी संकेत और इन्फ्लुएंजा / H1N1 मामलों की
प्रवृत्ति का पता लगाने के लिए की गई थी। जिला की स्वास्थ्य
देखभाल वितरण प्रणाली का मूल्यांकन इंफ्लुएंजा / H1N1 मामलों
के पहचान और प्रबंधन तथा इसे रोकने और नियंत्रित करने के लिए
प्रदान किए गए तकनीकी समर्थन के लिए किया गया था।
ए चक्रवर्ती ने जिला, नगरपालिका और क्षेत्रीय अस्पतालों,
जिले के आसपास के मेडिकल कॉलेजों सहित सभी संभावित स्थलों का
दौरा किया और अंत में उनका रिपोर्ट आंध्र प्रदेश में डीएमएचओ,
चित्तूर जिला और विजयवाड़ा के राज्य स्वास्थ्य विभाग के सचिव
को पेश किया । राज्य जांच सचिव के साथ बैठक में रिपोर्ट और
सिफारिशों के साथ यह जांच समाप्त हुई। राज्य के संबंधित
प्राधिकारी को प्रोफेलेक्टिक उपाय लेने का सुझाव दिया गया था।
भारत के पश्चिम बंगाल में Shigella sonnei के कारण
खाद्यजन्य संक्रमण का प्रकोप
प्रकोप जांच दल के सदस्य: एफ
देवनाथ, ए मुखोपाध्याय, एस दत्ता, जी चौधरी, आर नारायण साहा और
एपिडेमियोलॉजी डिवीजन के फील्ड सपोर्ट स्टाफ।
पश्चिम बंगाल के दक्षिण २४ परगना जिला, भंगौर द्वितीय ब्लॉक
के पाकापोल गांव से तीव्र गैस्ट्रोएंटेरिटिस (AGE) के साथ कुल
१९ शक्श को घरेलू पार्टी में खाना खाने के बाद संक्रामक रोग और
बेलियाघाटा जनरल अस्पताल, कोलकाता में भर्ती कराया गया था।
खाद्य संबंधी प्रकोप की घटना की पुष्टि करने के लिए NICED टीम
द्वारा एक महामारी विज्ञान और सूक्ष्मजीवविज्ञान जांच की गई
ताकि समय, स्थान और व्यक्ति के संदर्भ में इसका वर्णन तथा
प्रकोप का कारण निर्धारित किया जा सके जिसके पश्चात नियंत्रण
उपायों की सिफारिश संभव हो ।
हमने पार्टी के उपस्थित लोगों के बीच एक पूर्ववर्ती समूह
अध्ययन किया। हमने संस्थागत रूप से विकसित AGE सम्पर्कित केस
खोज प्रारूप का उपयोग कर जानकारी एकत्र की। मानक विधियों का
पालन करके बारह मामले के मरीजों के मल नमूने अलगाव और आंतरिक
रोगजनकों की पहचान के लिए संसाधित किए गए थे।
२३ नवंबर २०१६ को पार्टी में चौबीस लोगों ने भाग लिया और साथ
में दोपहर का खाना खाया।
खाद्य सेवन के समय से AGE मामलों के विकास के लिए औसत ऊष्मायन
(Median incubation) का अवधि १८.५ घंटे (IQR, १६.५ -२२ घंटे)
थी| कुल मिलाकर हमले की दर ७३ % (२५ /३४) थी, जिसमें से ७६ %
(१९ /२५ ) को अस्पताल में भर्ती की आवश्यकता थी। सभी आयु वर्ग
१०० % वसूली दर से प्रभावित थे। एक परोसा गया खाद्य पदार्थ
बीमारी से काफी महत्वपूर्ण था: टमाटर सलाद (RR = ४.१४ ; ९५ %
सीआई = १.२१ -१४.१३ )। आठ स्टूल नमूनों (६७ %; ८ /१२ ) को
Shigella sonnei के लिए सकारात्मक परीक्षण किया गया था। PFGE
विश्लेषण से पता चला है कि हाल में हुए प्रकोप में Shigella
sonnei उपभेदों को कोलकाता में स्थानीय रूप से परिचालित उपभेदों
से क्लोनिक रूप से संबंधित किया गया था|
हमने पुष्टि की है कि भोजन से उत्पन्न प्रकोप शिगेला सोननी के
कारण हुआ था और बचे हुए अपरिवर्तित रखे कच्चे टमाटर को इस
प्रकोप का मूल कारण के रूप से शिनाख्त किया जा सकता है |
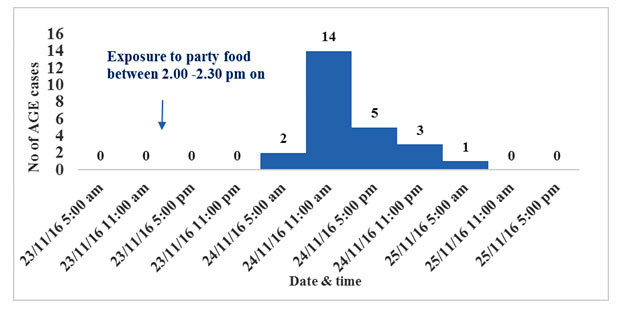
Fig 1: Distribution of Acute Gastroenteritis Cases,
food borne outbreak, Pakapol Village, Bhangore II, South 24
Parganas, West Bengal, India, 23rd - 25th November 2016

ICMR - NICED team visiting the affected family, Pakapol
Village, Bhangore II block, South 24 Parganas, November,
2016
बरानगर नगर क्षेत्र, २०१६ में डेंगू बुखार प्रकोप की
जांच
प्रकोप जांच दल के सदस्य: एफ देवनाथ और महामारी विज्ञान
विभाग के फील्ड स्टाफ
अगस्त २०१६ के दूसरे सप्ताह के दौरान, ICMR - राष्ट्रीय कॉलरा और आंत्र रोग संस्थान, कोलकाता को उत्तर २४ परगना जिला स्वास्थ्य प्राधिकरण ने बरानगर नगर पालिका में महामारी संबंधी जांच करने के लिए अनुरोध किया था| इसके प्रतिक्रिया के रूप में, ICMR-NICED ने संपूर्ण महामारी जांच की जिससे तीन प्रस्ताव सामने आया : १) स्थानीय स्वास्थ्य प्राधिकरण से रिकॉर्ड समीक्षा २) वार्ड १ में घर घर समीक्षा ३) बरानगर राज्य जनरल अस्पताल के अंदर / बाहर रोगी विभाग में केस खोज और पिछले तीन वर्षों में डेंगू की मासिक हमले दर की तुलना करके कोलकाता के नजदीक बरानगर नगर क्षेत्र में डेंगू बुखार के प्रकोप की पुष्टि | जुलाई २०१६ के आखिरी सप्ताह में प्रकोप शुरू हुआ और दिसंबर, २०१६ (छवि 2) के दूसरे सप्ताह तक जारी रहा। इस प्रकोप में कुल १६६० रोगी ने डेंगू के मामलों की पुष्टि की (सभी हमले की दर = ७ प्रति १००० ) और दो मौत (केस मौत = १ प्रति १०००) की सूचना मिली। ICMR-NICED ने NS1 ELISA/MAC ELISA परीक्षण के माध्यम से प्रमाणीकरण के लिए उस क्षेत्र के संभावित डेंगू मामले के रोगियों से 212 रक्त नमूने का परीक्षण किया और 1१६३ रक्त नमूने डेंगू के मामलों के रूप में सामने आए। इन १६३ डेंगू मामलों में से, ६३ मामलों के लिए सीरोटाइपिंग किया गया था और DEN 1 (६५ %, ४१ /६३ ) प्रमुख परिसंचरण सीरोटाइप था।
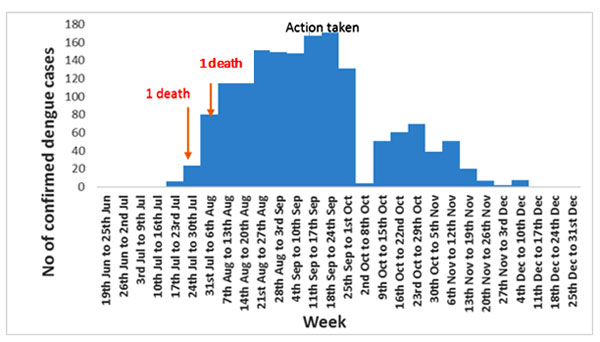
Fig 2: Distribution of dengue cases, Baranagar Municipality, July - December 2016

During training of the health workers of Baranagar
Municipality before starting house to house active case
search for dengue fever
प्रकोप जांच २०१५-१६
Wild Polio Viruses के प्रयोगशाला संरक्षण पर राष्ट्रीय कार्य बल (NTF ) कार्यक्रम में NICED का भागीदारी
यह संस्थान प्राथमिक रूप से दस्त के मरीजों से एकत्रित मल नमूनों से पृथक बैक्टीरिया, वायरल और परजीवी रोगजनकों पर काम करता है। यह संस्थान महामारी संबंधी निष्कर्षों को जोड़ने वाले टीका परीक्षणों का आयोजन के साथ साथ बैक्टीरियोलॉजी, वायरोलॉजी, पैरासिटोलॉजी, इम्यूनोलॉजी, आण्विक जीवविज्ञान और नैदानिक दवा के क्षेत्र में प्रयोगशाला आधारित विश्लेषण करता है । उपर्युक्त गतिविधियों को बनाए रखने के लिए, NICED प्रयोगशालाओं में विश्लेषण होने से पहले दस्त से प्रकोप प्रभावित इलाकों से मल के नमूनों और / या पानी के नमूनों की एक बड़ी संख्या एकत्र और संग्रहित की जा रही है। इसके अलावा, यह संस्थान स्वास्थ्य और परिवार कल्याण मंत्रालय, राज्य या केंद्र सरकार द्वारा अनुरोध किये जाने पर इंफ्लुएंजा वायरस संक्रमित नमूनों पर काम करता है । अनुसंधान / नैदानिक गतिविधियों के लिए एकत्र किए गए सभी नमूनों को Wild Polio Virus के प्रयोगशाला संरक्षण के दृष्टिकोण से राष्ट्रीय कार्य बल (NTF) द्वारा संभवतः पोलियो जोखिम सामग्री के तहत वर्गीकृत किया गया है।
NICED ने २०१२ में अपनी स्थापना के बाद भारत में Wild Polio
Viruses के प्रयोगशाला संरक्षण पर राष्ट्रीय कार्यक्रम में
सक्रिय रूप से भाग लिया। Wild Polio Viruses की प्रयोगशाला
रोकथाम के दृष्टिकोण से संभावित जोखिम को ध्यान में रखते हुए
को मल, पानी के नमूने, और नासोफैरेनजीजल swabs जैसे चिकित्सीय
नमूने के गैर भंडारण और विनाश पर विशेष ध्यान दिया गया है और
इन्हें NTF और ग्लोबल एक्शन प्लान (GAP) III प्रोटोकॉल (२०१४ )दिशानिर्देशों
के तहत चरण II गतिविधि का अनुपालन करना है ।
संस्थागत ?Wild Polio P2 Virus? की रोकथाम के लिए जोखिम आकलन
और जोखिम प्रबंधन समिति' का गठन ३ अगस्त, २०१५ को हुआ था। तब
से इस संस्थान ने समय-समय पर राष्ट्रीय समन्वयक, एनटीएफ को
रोकथाम की कार्रवाई रिपोर्ट जमा की। इन सभी गतिविधियों को 'ग्लोबल
पोलियो उन्मूलन और एंडगेम सामरिक योजना (पीईईएसपी) (२०१३-२०१८
)' के दिशानिर्देशों का पालन करना है। इसके अलावा, NTF के साथ
संयुक्त रूप से NICED ने १४ अगस्त, २०१५ को PEESP के महत्व पर
संवेदनशीलता के लिए एक बैठक की मेजबानी की और इस बैठक में कई
वरिष्ठ वैज्ञानिकों / संस्थानों / विश्वविद्यालयों के विभागों
के प्रमुखों ने भाग लिया जो संभावित पोलियो संक्रमित सामग्रियों
के साथ काम कर रहे हैं। अंत में, यह बताते हुए कि NICED फ्रीजर
में संभावित पोलियो संक्रमित सामग्रियों को संग्रहित नहीं कर
रहा है, अप्रैल २०१६ में एक सर्टिफिकेट (प्रमाण पत्र) जारी किया
गया है|
ए. पालित
पश्चिम बंगाल के विभिन्न दक्षिणी जिलों
में फैले दस्त के महामारी के प्रकोप (2015-16) के दौरान
पर्यावरणगत जीवाणुतत्व प्रयोगशाला द्वारा प्रकोप की जांच
(२०१५६-१६) , पश्चिम बंगाल के विभिन्न हिस्सों से माइक्रोबियल
विश्लेषण और पीने योग्य जल स्रोतों के नमूने की जांच तथा सरकारी
एजेंसियां को उनके परिणामों का रिपोर्टिंग करना, हमारी
पर्यावरण प्रयोगशाला की पर्यावरण प्रयोगशाला की नियमित गतिविधि
रही है| उत्तर २४ परगना, नदिया और हुगली, हावड़ा, कोलकाता और
इसके आसपास के क्षेत्रों के विभिन्न PHC से पानी के नमूने
प्राप्त हुआ है । राज्य स्वास्थ्य सचिवालय, सरकार की एक
प्रतिलिपि प्रदान करते हुए पश्चिम बंगाल के सम्बंधित एजेंसियों
को परिणाम रिपोर्ट दाखिल किया गया हैं। । रिपोर्ट के तहत अवधि
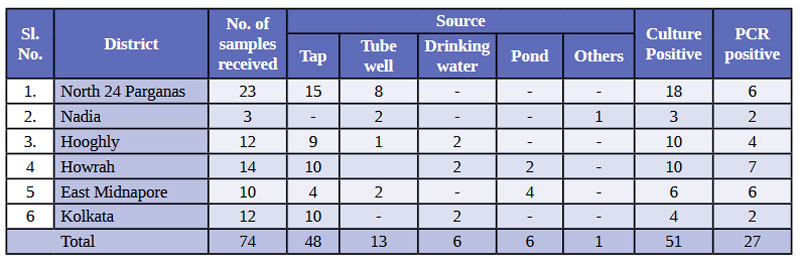
के दौरान, विभिन्न स्रोतों से ७४ नमूने प्राप्त हुए थे, जिनमें
से ५१ को मलीय कॉलिफॉर्म के लिए सकारात्मक पाया गया था और २७
को V. cholerae (तालिका 1) की उपस्थिति के लिए सकारात्मक पाया
गया था।
(Table 1) District-wise distribution of the Outbreak Water
Samples, their respective sources and identification of V. cholera
के सरकार
?किसी भी डेंगू प्रकोप और न्यू टाउन सिटी
में इसके नियंत्रण का अनुमान लगाने के लिए मच्छर से उत्पन्न
बीमारियों पर निगरानी? संक्रांत एक प्रस्ताव न्यू टाउन
डेवलपमेंट अथॉरिटी को आवश्यक वित्त पोषण के लिए सौंपा गया था|
इस प्रस्ताव को नए टाउन डेवलपमेंट अथॉरिटी द्वारा सिद्धांत रूप
में स्वीकार किया गया और वित्त पोषण की संभावना की समीक्षा की
जा रही है।
आलोक देब
इन्होने १-५ मार्च, २०१६ के दौरान
स्थानीय मंदिर में मूर्ति को समर्पित भेंटों की खपत के बाद २४
-परगना (उत्तर) के सशन ब्लॉक में हुई खाद्य-संबंधी दस्त की
बीमारी के बारे में डॉ शांता दत्ता के साथ एक प्रकोप की जांच
की| १००० से अधिक लोग अलग-अलग आयु समूह, जो ज्यादातर एक विशेष
गांव से थे और स्थानीय मंदिर में भगवान को चढ़ाए गए प्रसाद का
उपभोग करते थे, इसकी खपत के कुछ घंटों के भीतर दस्त और उल्टी
से बीमार पड़ गए। उनमें से कुछ लोगों को हल्के बुखार और
सिरदर्द भी हुआ । आईडी और बीजी अस्पताल, बेलीघाटा में लगभग 300
लोगों को भर्ती कराया गया था जिनसे 30 रोगियों से प्रासंगिक
जानकारी और मल नमूने एकत्र किए गए थे। प्रभावित भक्तों के बीच
वितरित भोजन का नमूना भी प्राप्त और परीक्षण किया गया था।
.
प्रकोप जांच २०१४-१५
एनआईसीईडी वैज्ञानिकों द्वारा अक्टूबर, 2014 के दौरान बारामुल्ला जिले, कश्मीर में बाढ़ के बाद सार्वजनिक स्वास्थ्य स्थिति का मूल्यांकन
श्रीनगर के उत्तर-पश्चिम में स्थित बारामुल्ला जिला बाद में बाढ़ से प्रभावित हुआ था - अधिकांशतः अतिप्रवाहित पानी के कारण जो श्रीनगर शहर को डुबोकर बर्बाद किया और कुछ हद तक भारी बारिश से हुए फ्लैशफ्लूड्स के कारण । बाढ़ के पानी प्रभावित क्षेत्रों में ठहराव के बिना केवल कुछ दिनों के अंदर उतर गए|
About 16% of the villages in the district were affected by the flood. However, most of these villages were affected mild-to-moderately; some villages in a few blocks were severely affected and required special attention. These flood hit areas were already visited by one or the other EMR teams and the district health system also responded very quickly and efficiently so that the health situations even in the hard-hit areas were never beyond control.
Except for an increase in number of dermatitis cases (following contacts with polluted flood water) in some areas and an increase of road traffic accident cases noted in the district hospital, there have been no outbreak of diseases so far in the district following the flood and at present there does not seem to have an imminent threat of any major outbreak in the flood-hit areas of the district.
As far as diarrheal diseases are concerned, there was no increase in such cases since the flood - rather the number of cases in most areas showed a gradual decrease. This was possibly due to the effect of several factors - no stagnation of water, persistent use of tanker water, boiled water or water treated with chlorine tablets at household levels, as well as ensuing winter season that could negatively affect occurrence of diarrheal diseases. The other major water source to the affected areas that were being supplied through the PHE department was recently checked for adequacy of chlorination and coliform count (MPN), and as per CMO of the district, was found suitable for human consumption. Thus, there was no report of any diarrheal outbreak in any part of the district and there seemed to be no threat for any imminent outbreak of such diseases either. However, one sporadic diarrhoeal sample collected from Archanderhama of Pattan was psotive for multidrug resistant Entero pathogenic E. coli. So, continuous vigil in this regard should be maintained.
 Temporary shelters for homeless people in village Bala, Kashmir
Temporary shelters for homeless people in village Bala, Kashmir
Inspection of allocated isolation facilities for Ebola Virus Disease Outbreak by NICED Scientists during November 2014
A visit was made to STNM Hospital, Gangtok on 23 Nov 2014 by the following two members Central Team to inspect the allocated isolation facilities for Ebola Virus Disease (EVD): (Dr. Satyajit Sen, Regional Director Kolkata, Regional office of Health & FW, GOI and Dr. Shanta Dutta, Scientist F, NICED (ICMR). As per Govt. Order D.28015/4/2014/EMR/Pt from M/o Health and Family Welfare, Govt. of India, DGHS, EMR dated 21 Nov 2014, the team members started their onward journey to Gangtok, Sikkim on 23 Nov 2014. Immediately after arrival the members started visiting the different units of the Hospital e,g, Emergency, Outdoor, laboratory etc. They also inspected the under construction isolation facility of the hospital for checking the level of preparedness for EVD. The major points have been covered in the completed checklist provided by the EMR, DGHS, M/O Health and FW. Briefly, STNM Hospital has allocated one area for the isolation facilities, which may not be the ideal for construction of such unit. As per Medical Superintendent, STNM Hospital, there is acute shortage of space/ land to build such unit. The current unit has been located at least 50 meters higher up than the general hospital, and stone curved stairs need to be used for transportation of EVD patients. The unit is within the hospital campus, but attached to many other Dept. of the hospital like Cancer Registry Unit, IDD cell and Diet Stores.
Outbreak Investigation 2012 -13
During the epidemic outbreaks (2012-13) of diarrhea spreading across different southern districts of West Bengal, microbial analysis and examination of samples of potable water sources, from different parts of West Bengal and reporting of results to the Govt. agencies, has been a routine activity of the environmental laboratory. Water samples had been received from different PHCs of N. 24 Pargana, S. 24 Pargana, Murshidabad and Hooghly as well as from endemic and epidemic affected Municipal wards under the Kolkata Municipal Corporation and its adjoining areas. Results have been conveyed to the respective agencies with a copy of the same to State Health secretariat, Govt. of West Bengal. During the period under report, 45 samples had been received from various sources of which 20 had been found to be positive for faecal coliforms and 12 for presence of V. cholerae O1 (Table 1).
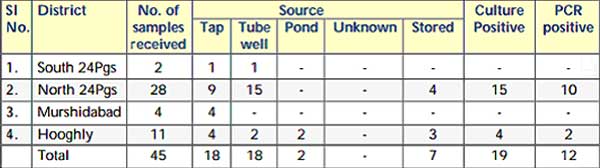 Analysis of Water/ Environmental Samples
Analysis of Water/ Environmental Samples
Outbreak Investigation 2011 - 12
Water and Environmental samples
During the focal diarrheal/cholera outbreaks (2011-12) in different southern districts of West Bengal, microbial analysis and examination of samples of potable water sources, from different districts of West Bengal as well as Municipal wards under Kolkata Municipal Corporation (KMC) and reporting of results to the Govt. agencies, has been a routine activity of the environmental laboratory.
Water samples had been received from different PHCs of N. 24 Parganas, S. 24 Parganas, Hooghly and Kolkata as well as from endemic and epidemic affected Municipal wards under the Kolkata Municipal Corporation and its adjoining areas. During the period under report, 47 samples had been received from various sources of which 39 had been found to be positive for fecal col iforms and 8 for presence of V. cholerae (Table 1).
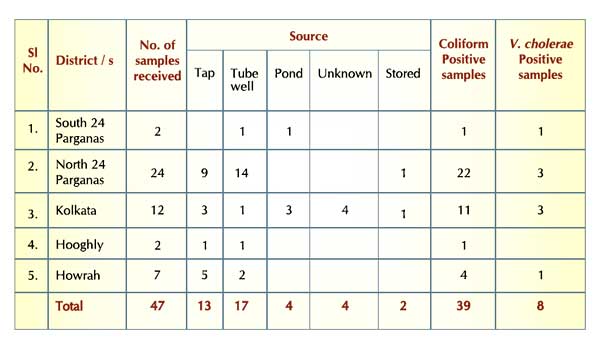 Analysis of Water/ Environmental Samples
Analysis of Water/ Environmental Samples
Outbreak Investigation 2010 - 11
Report of investigation of a cholera outbreak in Gujarat by team from National Institute of Cholera and Enteric Diseases, Kolkata, team from 31m May-2" June 2010
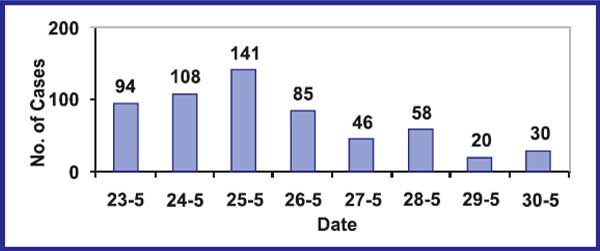
Acute Castro Enteritis (AGE) cases were reported since 23'd May from different villages of a block in Gujarat.
The week from 22nd May was marriage season during which time, there was large movements of groups of people from one village to another to attend the marriages. Most of the cases reported having attended one or other marriage ceremony. On returning to their homes, they fell ill and then spread the diseases to other members of the family. The temperatures had soared upto 48°C and there was acute scarcity of water. Since large amounts of water are required during the marriage ceremonies, water was bought in tankers from 2 open wells in Jhalod town. The wells are privately owned wells. The wells were visited by the team and were observed to be in dire state. The inside linings of the wells were not continuous with gaps in the walls where trees and other fungi and algae had grown. The water was obviously contaminated and the municipal authorities had instructed the owners to chlorinate the wells. In spite of these instructions, there was no residual chlorine in the well waters when the team tested the water with chloroscope. Instructions had also been given to chlorinate the water in the tankers but these also showed negative results for residual chlorine. Considering that the causative organism had been identified to be Vibrio cholerae, (transmitted through water), the cases mostly presented with acute watery diarrhoea with severe dehydration and the contaminated water source, it is highly suggestive of a water borne outbreak (rather than food poisoning as suspected initially). The team visited the several affected villages and interviewed some family members of diarrhoea cases. As expected, most cases reported having attended a marriage ceremony. Interestingly, there were two ladies who had attended different marriages and had only taken water but no food. They also had diarrhoea a nd stool was positive for Vibrio cholerae. This probably clinched the issue of water borne outbreak.
Laboratory report
Of 98 samples collected, 32 samples were positive for Vibrio cholerae. Antimicrobial susceptibility pattern was also tested. Of the 84 water samples sent for testing (collected from different sources of water), 50 were declared microbiologically unfit for drinking.
Recommendations advised
Most important recommendation was regular chlorination of wells and tankers supplying water to the community with routine monitoring with chloroscope for residual chlorine both at source and at the users' end.
Investigation of outbreaks of Acute Diarrhoeal Diseases (ADD)/Cholera in Rayagada and Kalahandi districts, Orissa,17-21 September 2010
At the request of the Director, Emergency Medical Relief, (EMR), Govt. of India, a team of NICER scientists went to Orissa to assist the state/ district health authorities in the investigation and control of outbreaks of acute diarrhoeal diseases (ADD)/ cholera in Rayagada and other districts of Orissa along with other experts from NCDC, New Delhi. The team visited the affected areas of Rayagada and Kalahandi districts along with senior officers from the Directorate of Health Services, Orissa and district officials during the period from 17 to 21 September, 2010.
Observations
A total of 1930 cases and 41 deaths were reported from district Rayagada in 2010 (upto 21 September). These cases occurred in 420 villages in 93 GPs of 8 Blocks. Rayagada district has reported the maximum number of cases and deaths in the state due to severe diarrhoea in 2010 (Tables 1,2)
Eight of 11 Blocks in Rayagada reported cases of severe diarrhoea in 2010. The worst affected blocks are Kalayansinghpur (704 cases, 8 deaths), Kashipur (365 cases, 10 deaths), Bisamacuttack (318 cases, 11 deaths), Jemadeipentha (269 cases, 2 deaths), Gudari (74 cases, 6 deaths) and Jagannathpur (85 cases, 4 deaths)
Analysis of 41 deaths in district Rayagada revealed that 10 deaths occurred in 6 villages of three sub-centres in Kashipur Block (including 4 deaths in village Bahardulki), 8 deaths occurred in 6 villages of two sub-centres in Ksinghpur block (including 2 deaths each in village Lekapai and Ksinghpur), and 11 deaths occurred in 6 villages of three sub-centres of Bisamacuttack block (including 4 deaths in village Gadaba, 2 deaths in village Goilkana). Thus multiple deaths occurred in some very small villages. Virtually all deaths occurred in homes (Table 1).
People were not aware of ORS, where is it available in the village and when and how to use it. Halogens tablets have been distributed in the affected areas, but most in the remote rural areas do not seem to use them in the absence of a strong IEC campaign.
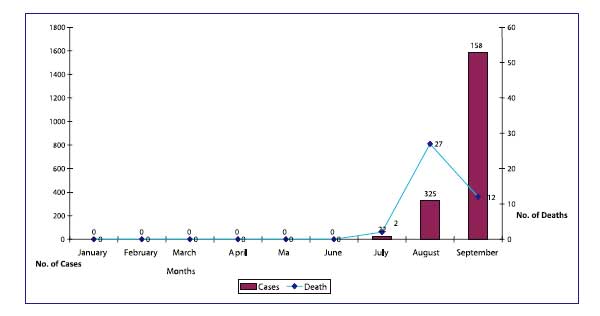 Month-wise Cases and Deaths due to severe diarrhoea in Rayagada district, Orissa, 2010 (up to 21st Sept)
Month-wise Cases and Deaths due to severe diarrhoea in Rayagada district, Orissa, 2010 (up to 21st Sept)
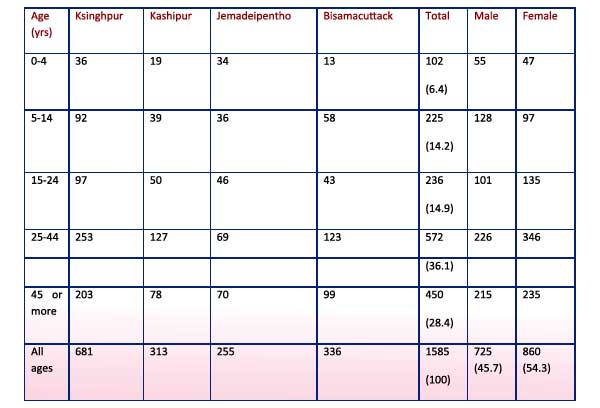 Cases of Severe diarrhoea indistrict Rayagada by age and sex, 2010
Cases of Severe diarrhoea indistrict Rayagada by age and sex, 2010
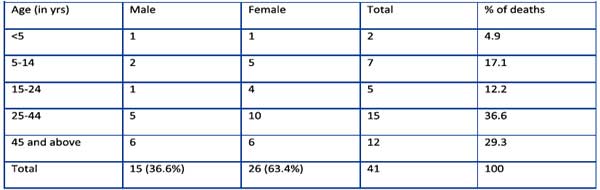 Deaths due to Severe diarrohea in district Rayagada by age and sex, 2010 (upto 21st Sept)
Deaths due to Severe diarrohea in district Rayagada by age and sex, 2010 (upto 21st Sept)
Analysis of age distribution of the deaths in Rayagada revealed that only 4.9% deaths occurred in under-five children and 78% deaths occurred in persons 15 years and above. Deaths in adults following dehydration usually indicate cholera. Male contributed to about 37% of deaths, the remaining 63% deaths occurred in females.
Clinical observations
The main presenting symptoms in outbreak associated cases are profuse painless watery diarrhoea, with or without vomiting, followed by dehydration. All these cases are managed with intravenous fluids (Ringer Lactate) and antibiotics like Norfloxacin, Ciprofloxacin, Ofloxacin and Tinidazole. None of them had received ORS at home; similarly none was given ORS solution in the treatment centre when they were being administered intravenous fluids.
प्रयोगशाला अवलोकन
अगस्त-सितंबर २०१० के दौरान, २० रेक्टल swabs रायगडा जिले से RMRC, भुवनेश्वर को भेजा गया था। २० में से ८ (४0%) नमूने कोलेरा के लिए सकारात्मक परीक्षण किया। अलगाव अजीथ्रोमाइसिन, नॉरफ्लोक्सासिन, सिप्रोफ्लोक्सासिन, क्लोरोम्फेनिकोल, नियोमाइसिन और जेनेटैमिसिन से संवेदनशील थे (बाद में ऑफलोक्सासिन और डोक्साइक्लिन को संवेदनशील माना गया), लेकिन एम्पिसिलिन, टेट्रासाइक्लिन, नालिडिक्सिकैसिड, फुराज़ोलिडोन, स्ट्रेप्टोमाइसिन, एरिथ्रोमाइसिन, को-ट्रिमोक्सज़ोल प्रतिरोधी थे। काशीपुर, कल्याणसिंहपुर, बिसामाकट्टाक और गुड़ारी के विभिन्न स्रोतों से १४ पानी के नमूने को भी RMRC में परीक्षण किए गए थे, लेकिन जिला कालाहांडी के विब्रियो कोलेराई नमूने के लिए कोई वृद्धि नहीं हुई थी| अगस्त-सितंबर २०१० के दौरान जिला कालाहांडी के ८ नमूने भी RMRC भुवनेश्वर में परीक्षण किए गए थे। उनमें से ५ (६३ %)को Vibrio cholerae 01 biotype Eltor Ogawa के लिए सकारात्मक पाए गए थे|
NICED, कोलकाता की प्रयोगशालाओं में १५ नमूने परीक्षण किए गए थे। १५ नमूनों में से ११ (७३ %) ने सकारात्मक परीक्षण किया (कालाहांडी मैं पाए एक इनाबा को छोडकर सभी Vibrio cholerae 01 biotype Eltor Ogawa थे)| सभी ११ अलगाव टेट्रासाइक्लिन, डोक्सीसाइक्लिन, सिप्रोफॉक्सैसीन, नॉरफ़ोल्सासिन, ऑफलोक्सासिन, एरिथ्रोमाइसिन और अजीथ्रोमाइसिन के प्रति संवेदनशील थे और एम्पिसिलिन, कोट्रिमॉक्सोजोल, फुराज़ोलिडेन और नालिडिक्सिक एसिड के प्रतिरोधी पाए गए थे।.
निष्कर्ष
चिकित्सकीय, महामारी विज्ञान और प्रयोगशाला जांच से रायगडा और कालाहांडी में कोलेरा के प्रकोप की पुष्टि करती है। हालांकि राज्य / जिला अधिकारी सुरक्षित जल प्रदान करने के प्रयास तथा बीमारीयों के इलाज के लिए सुविधाएं उपलब्ध कर रहे हैं और कोलेरा को नियंत्रित करने के लिए व्यक्तिगत और घरेलू स्वच्छता में सुधार के लिए जागरूकता बढ़ रही है, इसके बाबजूद प्रभावित इलाकों की दूरी, खराब परिवहन और संचार सुविधाओं ने शुरुआती पहचान कार्य और उपचार को मुश्किल बना दिया है जो की मृत्यु दर को रोकने के लिए आवश्यक हैं ।


